Introduction
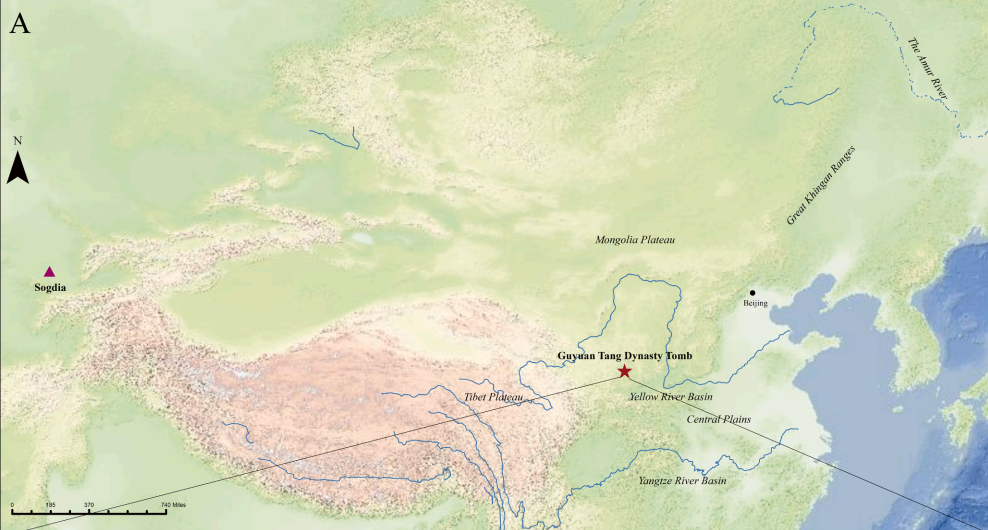
The Silk Road, active from the second century BCE to the fourteenth century CE, was a major trade route extending from Chang’an (modern Xi’an) in the east to the Mediterranean in the west, facilitating economic, cultural, and political exchanges between China and the Roman Empire. Its establishment during the Western Han Dynasty, particular lyunder the efforts of Zhang Qian (Christian, 2000), laid the foundation for centuries of interaction (Fuxi et al., 2009). The Tang Dynasty (618–907CE) marked the peak of Silk Road activity, often referred to as its“Golden Age,” characterized by economic and social flourishing (Zhao et al., 2023). As the Tang capital, Chang’an became a crucial hub,fostering the movement of goods, ideas, and people.The Sogdians, an Iranic-speaking people from Sogdiana (present-dayUzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan), were among the diverse communities thriving along the Silk Road (Xie 2023). Chinese records, such as the “Wei Shu” (魏书), refer to them as the Zhaowu Nine Surnames(“昭武九姓”) (Gao 2019). The Sogdians used their strategic geographic to facilitate trade and cultural exchange, creating a vibrant merchant society that significantly influenced the dissemination of religion and art between China and the West.During the Wei Jin to Sui Tang Dynasties (266–907 CE), many Sogdians settled in China (Ma 2016). Over generations, they assimilated into local communities while leaving a lasting cultural legacy. The region of Guyuan, northwest of Xi’an, was a critical nexus of ethnic integration during the Tang Dynasty, attracting diverse groups since the
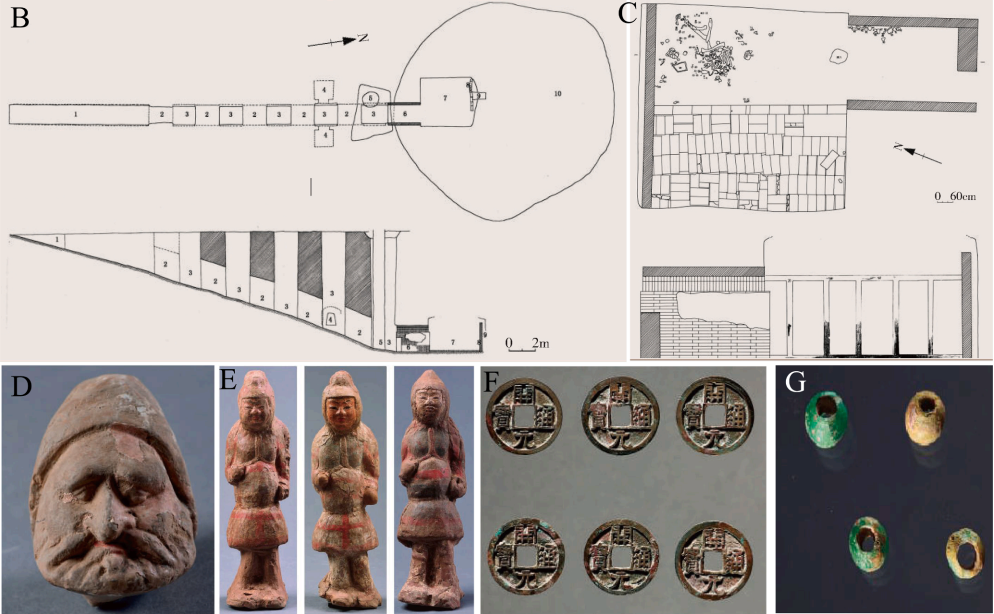
Western Zhou Dynasty. The Guyuan Tang Dynasty tomb (M1401) contains artifacts with Sogdian cultural elements, such as figurines and metalwork (Zhu et al., 2022). However, skeletal remains associated with Sogdians are scarce, and no genomic data have been previously published, limiting our understanding of their origins and interactions with local populations. Recent discoveries, including tomb M1401, provide a unique opportunity to explore the genetic history of Sogdians during this period.